Advanced Robotic Solutions for Active Living.
Offering state-of-the-art robotic joint replacement that enhances surgical precision and recovery outcomes. Designed to restore mobility and support an active, pain-free lifestyle with minimal downtime.
Known for his warm, approachable nature and clear, friendly communication, he ensures that every patient feels heard, understood, and supported throughout their treatment journey. Dr. Mrinal is a highly trained and compassionate orthopaedic surgeon with a deep commitment to patient care. He takes time to explain diagnoses and treatment plans in detail, empowering patients to make informed decisions. He believes that surgery is only one part of healing — for him, recovery truly begins after the procedure. That’s why he places strong emphasis on post-operative rehabilitation, working closely with each patient to help them regain full function and return to an active life.
Know More Book Appointment
Dr. Mrinal Prakash is well-trained with strong academic qualifications and advanced fellowships in orthopaedics.
Dr. Mrinal Prakash brings extensive surgical experience from leading hospitals and institutes.
Dr. Mrinal Prakash has contributed to renowned medical journals with impactful orthopaedic research.


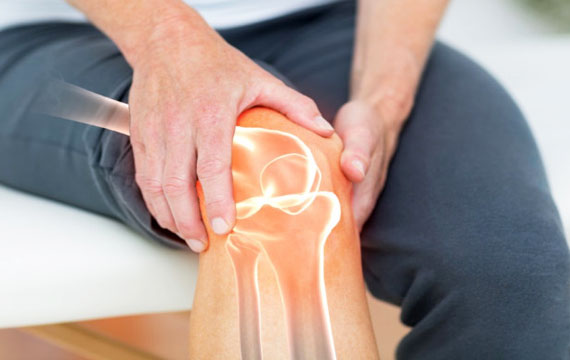
Joint replacement surgery is recommended when severe joint damage (usually from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or injury) causes persistent pain and disability despite non-surgical treatments.
If you:
Early consultation can prevent worsening deformity and ensure better recovery outcomes.
Most patients can walk with support within 24–48 hours after knee or hip replacement surgery.
Commitment to post-surgery rehabilitation plays a major role in long-term success.
Modern techniques, including minimally invasive approaches, regional anaesthesia, and multimodal pain management, greatly reduce post-surgical discomfort.
Most patients report that post-surgery pain is less than the arthritis pain they experienced before the procedure — and it improves steadily with rehab.
In my personal cases, I stop all injectable antibiotics and analgesics (pain killers) 48 hours after surgery. Patient get discharged from the hospital 48-72 hours after surgery, once they are comfortably walking.
Robotic-assisted joint replacement allows for more precise implant positioning, better alignment, and customized planning based on a patient’s anatomy.
Benefits include:
Robotics is a tool — not a replacement for the surgeon’s skill. Always choose a surgeon with specialised training in robotic and conventional joint replacement techniques.
Modern implants last 15–20 years or more with proper care.
Factors affecting lifespan include:
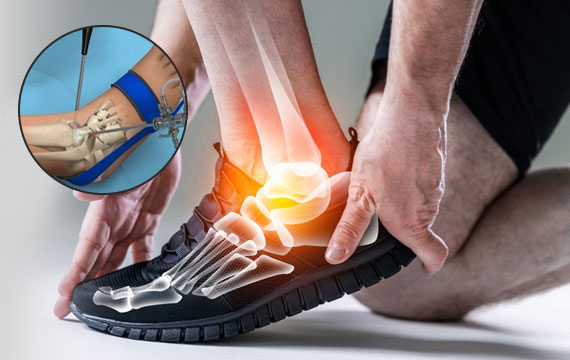
Follow the R.I.C.E. protocol:
When to see a doctor immediately:
Early orthopaedic evaluation helps prevent chronic ligament or cartilage damage.
No. Not all ligament tears require surgery.
Factors to consider:
In young athletes, delaying surgery for unstable ligament injuries can lead to more damage over time.
Recovery after ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) reconstruction depends on the surgical technique, the patient’s overall health, and their commitment to rehabilitation.
Typical recovery timeline:
Yes — in many cases, untreated ligament injuries (especially ACL or PCL tears) can lead to joint instability, causing repeated episodes of the knee giving way.
This instability increases wear on the cartilage and meniscus, accelerating joint degeneration and leading to early-onset osteoarthritis.
Who is at risk:
Local context: In active communities like Mumbai and Thane, untreated ligament injuries in younger years often present as severe arthritis by the age of 40–45.
Preventing sports injuries starts with education and proper training.
Key tips: